Definition
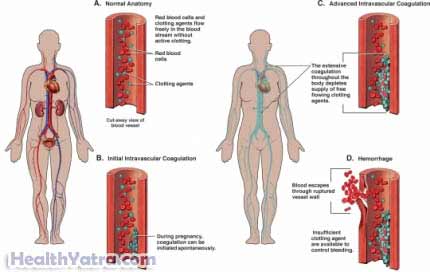
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a problem with how your blood clots. DIC causes blood clots to form in small blood vessels. These clots can slow or block the flow of blood through these vessels. The organs and tissue that rely on this blood flow can then be damaged.
Blood clots are made of platelets and clotting factors. The blood clots caused by DIC decrease the body’s platelets and clotting factor. This could lead to bleeding in other areas of the body.
DIC may be acute or chronic. Acute DIC develops over a few hours or days. I can quickly lead to bleeding problems. Chronic DIC can develop over months. It is most often caused by cancer. Chronic DIC develops blood clots but rarely leads to bleeding problems. DIC is a life-threatening condition that must be treated right away.
Causes
DIC is caused by other medical conditions or injuries. The trauma or inflammation caused by these conditions stimulates changes in the blood clotting process.
DIC can also be caused by toxin from a poisonous snakes but this cause is rare.
Risk Factors
Factors that may increase your chance of DIC include:
- Sepsis—a body-wide infection
- Complications of pregnancy and delivery such as :
- Eclampsia
- Amniotic fluid clots
- Retained placenta
- Recent trauma such as:
- Burns
- Head injury
- Frostbite
- Recent surgery
- Cancer including leukemia
- Severe liver disease or pancreatitis
Symptoms
Symptoms of DIC can vary because the blood clots can occur throughout the body. Clots in the:
- Brain may cause headaches, dizziness and other signs of stroke such as speech and movement problems
- Legs may cause swelling, redness, and warmth
- Lungs can cause shortness of breath
- Heart can cause chest pain or a heart attack
Bleeding is often the first sign in acute DIC. Signs of bleeding include:
- Bruising that is more frequent or severe than expected
- Red spots on skin (look like series of tiny bruises)
- Excess bleeding from wounds
- Nosebleeds
- Bleeding from gums
- Blood in urine—may cause pink or brown urine
- Dark, tarry stool
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
If you have bleeding that does not stop or unexplained bleeding get emergency care.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about symptoms and medical history. Blood test will also be done to look for abnormal levels of clotting factors and platelets.
Treatment
The underlying cause of DIC will need to be identified and treated. These treatments will vary by conditions.
To help manage the DIC itself your doctor may recommend:
- Blood products—to help restore clotting factors balance. You may be given fresh frozen plasma, platelets, or cryoprecipitates.
- Heparin—medication that thins the blood. It may be given in combination with blood products to reduce blood clots.
- Antithrombin III—medication used to slow down clotting in certain patients.
Prevention
Prompt treatment for any of the conditions associated with DIC may reduce your risk for DIC.