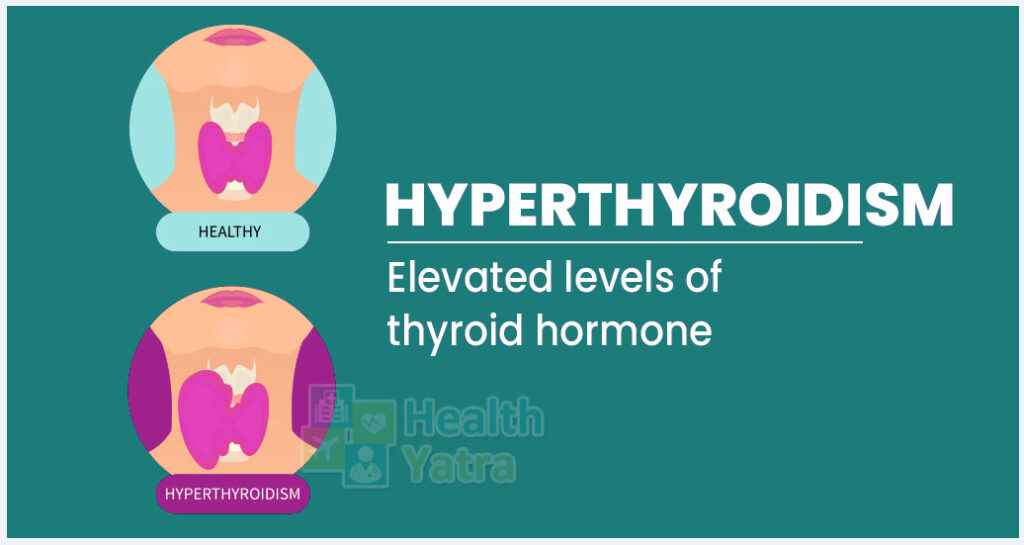
Hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid is a medical condition in which the thyroid gland produces too much of thyroxine hormone. Hyperthyroidism thereby can significantly accelerate metabolism of the body & cause sweating, irritability, nervousness, sudden weight loss & a irregular or rapid heartbeat. Several treatment options are available for patients suffering from hyperthyroidism. Doctors commonly use anti-thyroid medications & radioactive iodine so as to slow production of hormones in thyroid gland. Sometimes, treatment of overactive thyroid may also involve surgery in order to remove part or all of the thyroid gland. Although most people respond well to hyperthyroidism treatment when it is diagnosed, it can also be serious if left untreated or ignored.
Signs & Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Quite often hyperthyroidism can efficiently mimic other health problems & which may make it difficult for doctors to diagnose. Overactive thyroid can cause a variety of signs & symptoms including the following.
- Sudden loss of weight, even when appetite, amount & type of food eaten remains the same or even increases
- Tachycardia or rapid heartbeat which is commonly more than 100 beats a minute
- Arrhythmia or irregular heartbeat or palpitations, which is pounding of the heart
- Increase in appetite
- Irritability, anxiety & nervousness
- Tremor, which is usually a fine trembling feeling in fingers & hand
- Sweating
- Changes in patterns of menstruation
- Increase in sensitivity to heat
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Muscle weakness & fatigue
- Goiter – enlarged thyroid gland which may appear as swelling at the base of neck
- Bowel pattern change with more frequent bowel movements
- Fine & brittle hair
- Thinning of skin
Older hyperthyroidism adult patients are more likely to have subtle symptoms or no signs of overactive thyroid symptoms. Subtle symptoms can include an increased heart rate, tendency to become tired during ordinary daily activities & intolerance to heat. Medications which are known as beta blockers & are commonly used in treatment of high blood pressure & various other conditions can easily mask many signs & symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
Graves’ Ophthalmopathy
Sometimes, a fairly uncommon problem known as Graves’ Ophthalmopathy may affect eyes of hyperthyroidism patients, especially if they indulge in smoking. Eyeballs in this condition are found to protrude beyond the normal protective orbits in this disorder when muscles & tissues swell behind the eyes. This will push forward eyeballs so far that they actually bulge out of their orbits & thereby causing the front surface of eyeballs to become dry. However, eye problems most often improve without any treatment.
Signs & Symptoms of Graves’ Ophthalmopathy
- Swollen or Red Eyes
- Protruding Eyeballs
- Light Sensitivity
- Blurry or Double Vision
- Inflammation or Reduced Eye Movement
- Excessive Discomfort or Tearing in One or Both Eyes
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
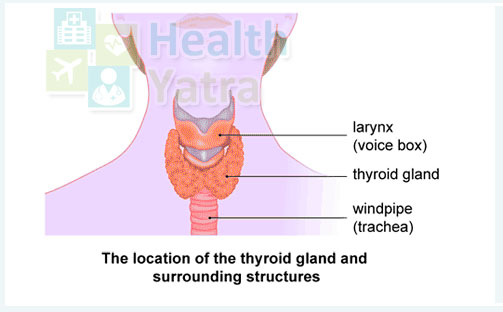
A number of medical conditions including thyroiditis, toxic multinodular goiter or Plummer’s disease, toxic adenoma or Graves’ disease can cause hyperthyroidism. Thyroid is basically a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. Even though it weighs less than an ounce, thyroid gland produces an enormous impact on health. Every little aspect of metabolism in the human system is regulated by hormones produced by the thyroid gland.
Hormones Produced by Thyroid Gland
Thyroxine (T-4) & Triiodothyronine (T-3) are the two main hormones produced by the thyroid gland. These influence almost every cell within the human body. They effectively maintain rate at which body uses carbohydrates & fats, help control temperature of the body, influence the heart rate & regulate production of protein. Thyroid gland also produces another hormone called calcitonin which helps regulate amount of calcium in blood.
Overall Working of Thyroid Gland
The rate at which T-3 & T-4 are released is pragmatically controlled by pituitary gland which is located in hypothalamus, an area at the base of brain which acts as a thermostat for the entire system. Hypothalamus signals pituitary gland to make a hormone called thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH. Pituitary gland will then release TSH, the amount of which depends upon the quantity of T-3 & T-4 in blood. TSH is programmed to rise when patients do not have enough T-3 & T-4 in blood. Similarly, high levels of T-3 & T-4 in blood will make TSH levels fall. Finally, it is the thyroid gland which will regulate production of hormones based upon the amount of TSH it receives through blood. When thyroid gland is diseased & is releasing large amounts of thyroid hormone on its own, TSH level in blood will invariably remain below normal. Similarly, if the diseased thyroid gland will not make enough thyroid hormone, TSH level in blood will effectively remain high.
Common Reasons for Producing Excessive Thyroxine (T-4)
Normally, thyroid gland releases the right amount of hormones required by the body, but there are times when it produces too much of T-4 hormone. This usually occurs due to a number of reasons including some of the following.
- Graves’ Disease – This is an autoimmune disorder wherein antibodies produced by the immune system stimulate thyroid to produce excessive T-4. This is considered as one of the most common causes of hyperthyroidism. Normally, immune system utilizes antibodies to protect against bacteria, viruses & various other foreign substances which are found to invade the body. These antibodies mistakenly attack the thyroid gland & occasionally attack tissue behind eyes (Graves’ Ophthalmopathy) & skin mostly within the lower leg & shins (Graves’ Dermopathy) in Graves’ disease. Scientists are yet not sure as to what causes Graves’ disease, though several factors including a genetic predisposition are most likely involved.
- Toxic Adenoma / Toxic Multinodular Goiter / Plummer’s Disease (Hyper-functioning of Thyroid Nodules – This is a type of hyperthyroidism which occurs when one or more adenomas of thyroid gland produce excessive T-4. Adenoma is part of the thyroid gland which has walled itself from the main gland by forming benign (noncancerous) lumps which may also cause enlargement of thyroid gland. However, not all adenomas produce too much T-4 & doctors are yet not sure as to what cause some adenomas to start producing excessive T-4 hormone.
- Thyroiditis – Quite often, thyroid gland can become inflamed for reasons unknown. This inflammation can cause excessive storage of thyroid hormone in the gland to leak into bloodstream. Subacute Granulomatous Thyroiditis is a rare type of thyroiditis which causes pain in thyroid gland. Other types of thyroiditis like Postpartum Thyroiditis are painless & may sometimes occur after pregnancy.
Time to See a Doctor for Overactive Thyroid Gland
It is a sensible time to consult a doctor when people experience an unexplained loss of weight, unusual sweating & swelling at the base of neck, rapid heartbeat and/or other symptoms which are associated with hyperthyroidism. Moreover, it is quite important that patients elaborately describe changes that they have observed, since many signs & symptoms of hyperthyroidism may also be associated with a number of other health conditions. In case the patient has earlier been treated or is currently being treated for hyperthyroidism, they are advised to regularly see the doctor so as to enable him or her monitor their condition.
Preparing for Initial Appointment for Hyperthyroidism
Family doctors in these conditions usually immediately refer such cases to an endocrinologist who specializes in hormone-secreting glands of the body. Patients who are having involvement of the eye may also be referred to an ophthalmologist. Nevertheless, it is sensible to prepare for initial appointment in any case. Some information so as to help prepare patients for initial appointment & to know what they can expect from the doctor are listed below.
What Patients are required to Do?
- Keep Aware of Any Pre-Appointment Restrictions – When patients make initial appointments for hyperthyroidism, they should check with the doctors if there is anything they need to do in advance, like fasting.
- Write Down Symptoms Experienced – This should also include anything which may seem unrelated to reason for which patient’s have scheduled this initial appointment.
- Jot Down Key Personal Information – This will include any major stress or any recent changes in patient’s life.
- Keep a List of All Medications – Including all supplements & vitamins patient is taking.
- Let a Family Member or Friend Accompany Patient – Somebody who is accompanying the patient will be helpful in remembering information which the patient may miss or forget during consultation.
- Jot Down Questions to Ask Doctors – This will help patients remember them during initial appointment.
List of Questions Patients Can Ask Doctors
The following list of questions will help patients make the most of the time they spend with the doctor during initial appointment for hyperthyroidism.
- What is it that is most likely causing this condition or symptoms?
- Are there any other causes for my condition or symptoms?
- What tests will I need to undergo?
- Is my hyperthyroidism condition temporary or chronic?
- Which is the best course of action in my case?
- Are there any other alternatives to the primary approach you are suggesting?
- How can I manage my other health conditions along with hyperthyroidism?
- Are there any restrictions which I will need to follow?
- Should I seek another specialist doctor for my condition?
- Are there any generic alternatives to the medicines you are prescribing?
- Can you provide me brochures or other printed material for my information?
- Which websites do you recommend for me to visit?
- Ask as many other relevant questions that you can think of.
What Doctors Usually Ask Patients?
Doctors are most likely to ask a number of questions to the patients including some of them or all which are mentioned below.
- When did you start having these symptoms?
- Have these symptoms been occasional or continuous?
- How severe are these symptoms?
- What is it, if anything, that seems to improve symptoms?
- What is it, if anything, which worsens symptoms?
- Do any other members of your family have or have ever had thyroid disease?
- Have you in recent past undergone any radiology scans which used intravenous contrast?
Tests & Diagnosis for Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed by taking the following steps.
- Medical History & Physical Examination – Doctors may try & detect a slight tremor in fingers when they are extended, warm & moist skin, changes in eye & overactive reflexes during physical examination. Doctors will also examine the thyroid gland as patients swallow so as to see if they are bumpy, enlarged or tender & check the pulse of the patient in order to find out if it is rapid.
- Blood Tests – Diagnosis of hyperthyroidism is usually confirmed with blood tests that can effectively measure levels of TSH & thyroxine in blood. Low or non-existent amounts of TSH & high levels of thyroxine indicate existence of an overactive thyroid. Amount of TSH is very important simply because this is the hormone which naturally signals thyroid gland to produce more of thyroxine. These blood tests are particularly necessary for older adults who may not be displaying classic symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
When blood tests positively indicate hyperthyroidism, doctors may indicate any one of the following tests so as to help them determine why thyroid gland of the patient is overactive.
- Radio Iodine Uptake Test – This test involves taking a small oral dose of radioactive iodine known as radioiodine. Iodine collects in thyroid gland over time because thyroid makes use of iodine in order to manufacture hormones. Patients are normally checked after two, six or 24 hours, & sometimes after all these three time periods, so as to determine how much of iodine has been absorbed by the thyroid gland. High uptake of radioiodine indicates that the thyroid gland is producing large amounts of thyroxine. Most likely cause of this could either be hyper-functioning nodules of thyroid or Graves’ disease. When patients are having hyperthyroidism even when radioiodine uptake is low will indicate that thyroxine stored inside the thyroid gland is leaking into the bloodstream & will invariably indicate a condition called thyroiditis. Knowing what exactly is causing hyperthyroidism, will enable doctors plan the most appropriate treatment. Although, radioiodine uptake test is in no way uncomfortable, but will eventually expose patients to small amounts of radiation.
- Thyroid Scan – Hyperthyroidism patients will have a radioactive isotope injected into vein on the inside of elbow or sometimes into a vein in hand during this test. Patients will then have to lie on a table with their head stretched backward so as to expose the neck area. A special camera is used to produce an image of thyroid gland onto a computer screen. Requirement of time for this procedure may vary depending upon how long the isotope takes to reach the thyroid gland. Patients may also have some discomfort in the neck with this test & will also be exposed to small amounts of radiation during this test. Many a times thyroid scan is a part of the radioiodine uptake test. In such a case it is the orally administered radioactive iodine which is used for imaging thyroid gland.
Treatments for Hyperthyroidism
Although several treatments for hyperthyroidism are available, the best approach however depends upon the physical condition, age, underlying cause, personal preference & severity of disorder in the patient.
- Radioactive Iodine – Radioactive iodine is absorbed by the thyroid gland when taken orally by mouth. Subsequently, it will cause thyroid gland to shrink & symptoms to subside, most usually within 3 – 6 months of time. Since this treatment causes considerable slowing down of thyroid activity, it may result in hypothyroidism, which is a condition associated with underactive thyroid gland. Eventually, patients may need medication to be taken every day so as to replace thyroxine. Radioactive iodine has generally shown to be safe & has been in use for more than 60 years as treatment for hyperthyroidism.
- Anti-Thyroid Medications – These medications will gradually reduce symptoms of hyperthyroidism by preventing thyroid gland from producing excessive amounts of hormones. These types of medications include methimazole (Tapazole) & propylthiouracil. Overactive thyroid gland symptoms usually begin to improve within 6 – 12 weeks but these treatments typically continue for at least one year & often longer periods of time. This usually clears up the problem for some people while others may experience a relapse. Both these drugs also can cause serious damage to liver & sometimes may even lead to death. Since propylthiouracil has caused more liver damage in more number of cases, it should generally be used only when methimazole cannot be tolerated by hyperthyroidism patients. Moreover, a small number of patients are also allergic to these drugs & may therefore develop joint pain, fever, hives & skin rashes. These drugs also make patients more susceptible to infection.
- Beta Blockers – Commonly used to treat high blood pressure, beta blockers will not reduce levels of thyroid hormones but can effectively reduce rapid heart rate so as to help prevent palpitations. This is the reason doctors often prescribe them to help patients feel better until thyroid hormone levels return close to normal. Side effects of beta blockers include dizziness, diarrhea, constipation, upset stomach, headache & fatigue.
- Thyroidectomy Surgery – Although this is an option for a select few cases, some hyperthyroidism patients are good candidates for thyroid surgery if they are pregnant or otherwise cannot tolerate anti-thyroid drugs or do not want to or cannot undergo radioactive iodine therapy as treatment. Surgeons will remove most of the thyroid gland during thyroidectomy surgery. Risks associated with thyroid surgery include damage to parathyroid glands & vocal cords. Parathyroid glands are four tiny glands which are situated on the back of thyroid gland & help in controlling level of calcium in blood. Moreover, thyroidectomy patients will also additionally need lifelong levothyroxine (Synthroid, Levoxyl) treatment in order to supply normal amounts of thyroid hormone to the body. In case parathyroid glands are also removed, patients will further need more medication so as to maintain normal blood-calcium levels.
Managing Graves’ Ophthalmopathy
Patients can manage mild signs & symptoms of this type of Graves’ disease by avoiding bright lights & wind & by using lubricating gels & using artificial tears. In case symptoms are more severe, doctors usually recommend treatment with corticosteroids like prednisone in order to reduce swelling behind eyeballs. Surgical procedure may be the only suitable option in certain cases.
- Orbital Decompression Surgery – Doctors remove the bone between sinuses & eye socket in this surgical procedure. Sinuses are basically air-spaces located next to the eye sockets. When this procedure is successfully completed, it improves vision & provides room for eyes to return to normal position. However, there are risks of complication associated with orbital decompression surgery including persisting or appearing double vision following surgery.
- Eye Muscle Surgery – Scar tissue from Graves’ Ophthalmopathy can sometimes cause one or more eye muscles which are too short. This will eventually pull eyes out of alignment & may lead to double vision. Eye muscle surgery can effectively help correct double vision by cutting the affected muscle from eyeball & reattaching the same further back. Goal of this surgical intervention is to achieve single vision while reading & looking straight forward. However, in some cases Graves’ ophthalmopathy patients may require more than one surgical operation so as to attain these results.
Lifestyle & Home Remedies for Hyperthyroidism
Once hyperthyroidism patients begin treatment, symptoms would subside & they will start feeling much better. Following suggestions can also be helpful in enhancing the healing process.
- Check with Doctors About Diet Supplements – Patients who have experienced muscle wasting or lost a great deal of weight may benefit from adding extra protein & calories to diet. Dietitians or doctors can help them with meal planning. However, in most cases they will not need to continue supplementing diet once their hyperthyroidism is under control. Hyperthyroidism treatment can also eventually contribute to weight gain. Therefore it is important to learn how to get as much nutrition as possible from food without adding extra calories. Eating the right amount of calcium & sodium are important dietary considerations for people with overactive thyroid.
- Getting Enough Vitamin D & Calcium – Since hyperthyroidism can also contribute to thinning of bones, it is extremely important for patients to get enough calcium every day so as to help them prevent osteoporosis. Recommended dosage is 1,000 milligrams of calcium everyday for adults between the ages of 19 – 50 years & men between 51 – 70 years. Calcium recommendation however increases to 1,200 milligram everyday for women aged 51 years or older or men aged 71 years or older. 600 international units (IUs) of vitamin D everyday is also recommended for adults aged between 19 – 70 years & 800 IUs everyday for adults 71 years & older. Hyperthyroidism patients should talk to their doctors about appropriate dietary & supplement guidelines so as to maintain health.
Taking Care of Graves’ Disease
Following suggestions may come helpful to soothe eyes & skin for hyperthyroidism patients having Graves’ Ophthalmopathy or Graves’ Dermopathy.
- Apply Cool Compresses to Eyes – Adding extra moisture to eyes will effectively provide relief.
- Wear Sunglasses – When Graves’ Ophthalmopathy patient’s eyes protrude, they are more vulnerable to ultraviolet rays & are also more sensitive to sunlight. Therefore, wearing sunglasses will help protect them from both wind & sun.
- Use Lubricating Eye Drops – Using eye drops in this situation will help relieve both scratchiness & dryness. However, make sure to use eye drops which do not contain redness removers. Since eyelids do not cover the entire eye while sleeping, a lubricating gel will be more useful before bed so as to prevent cornea from drying out.
- Elevate head of Bed – Keeping head higher than rest of the body will reduce swelling & eventually help relieve pressure on Graves’ Ophthalmopathy patient’s eyes.
- Over-the-Counter Creams for Swollen Skin – These creams containing hydrocortisone (Cortaid) will help relieve redness & swelling of skin on shins & feet. Talk to a pharmacist for finding such over-the-counter creams.
Hyperthyroidism Risk Factors & Complications
Hyperthyroidism, more particularly Graves’ disease tends to run in the family but is more common among women than men. Therefore, people should talk to the doctor about what it may mean to their health & for recommendations for monitoring their thyroid functions if any other member of the family is having hyperthyroidism.
Complications Associated with Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can eventually lead to a number of complications in patients including some of the following.
- Heart Problems – Most serious complications associated with hyperthyroidism involve the patient’s heart. Some of which include a rapid heart rate, atrial fibrillation which is a heart rhythm disorder & congestive heart failure in which the patient’s heart cannot circulate enough blood so as to meet the requirements of the body. Many of these complications are generally reversible with appropriate treatments.
- Brittle Bones – Hyperthyroidism, when left untreated will lead to osteoporosis, a condition with weak & brittle bones. The strength of bones in part depends upon the amount of calcium & other minerals they contain. Excessive amounts of thyroid hormones interfere with the ability of the body to incorporate calcium into bones.
- Eye Problems – Hyperthyroidism patients with Graves’ ophthalmopathy invariably develop eye problems including bulging, blurring or double vision & swollen or red eyes which are sensitive to light. Moreover, when left untreated, severe eye problems can also lead to loss of vision.
- Red & Swollen Skin – In some rare cases, people with hyperthyroidism suffering from Graves’ disease develop Graves’ dermopathy. Graves’ dermopathy is a condition which affects the skin by causing swelling & redness most often on shins & feet.
- Thyrotoxic Crisis – Hyperthyroidism patients are also at a risk of developing a condition called thyrotoxic crisis, which is a sudden intensification of symptoms leading to fever, rapid pulse & even delirium at times. Patients must seek immediate medical care in case this occurs.
Coping & Support for Hyperthyroidism Patients
One of the most important things for people diagnosed with hyperthyroidism is to receive the most appropriate medical care. When patients have decided on a course of action in consultation with their doctors, there are some additional things they can do which will help them effectively cope with this condition & support the body through the process of healing.
- Regular Exercise – Exercise will generally help hyperthyroidism patients feel better & improve their muscle tone along with the cardiovascular system. Moreover, weight-bearing exercise is important for patients with Graves’ disease simply because it will help maintain bone density. Exercise may also help these patients with reduced appetite alongside increasing their energy level.
- Relaxation Techniques – Several relaxation techniques can help maintain a positive look, especially when they are coping with illness like hyperthyroidism. It is a well documented fact that stress is a risk factor in Graves’ disease, therefore learning to relax & achieving balance in life can dramatically help maintain physical & mental well-being while coping with hyperthyroidism.
Affordable Treatment for Hyperthyroidism in India
Good news is that hyperthyroidism can be effectively treated. Although, this may take a while to get hormone levels back to normal balance, recovery can however be a smooth process when patients work with reputed endocrinologists if possible. India is an excellent global healthcare tourism destination which can provide a wide spectrum of affordable medical solutions including treatments for hyperthyroidism for people from all around the world. Healthcare infrastructure in the country is at par with the best in the world & so quite capable of delivering high-quality of treatments. Many doctors & surgeons practicing in India have initially been qualified & trained in western countries like the UK, Canada & United States before heading back to their homeland. HealthYatra is one of the most reputed online medical tourism platform which is associated with the best hospital facilities & top surgeons in the country, offering a variety of low cost healthcare solutions to international patient. Seamless services offered by HealthYatra include assisting in obtaining medical visa, online consultation, warm reception at airport on arrival, convenient travel & comfortable accommodation, scheduled appointments & medical procedures without any waiting period, exotic recuperative holiday option, follow-up checks & a successful farewell.
KEYWORDS: what is the best treatment for hyperthyroidism, i cured my hyperthyroidism, how to.cure hyperthyroidism permanently, hyperthyroidism medication hyperthyroidism treatment, hyperthyroidism diet, hyperthyroidism symptoms in females, levothyroxine for hyperthyroidism, hyperthyroidism treatment in india, what is the best treatment for hyperthyroidism, how to.cure hyperthyroidism permanently, hyperthyroidism: treatment guidelines, i cured my hyperthyroidism, is hyperthyroidism curable, hyperthyroidism test, hyperthyroidism causes, hyperthyroidism diet