Definition
An intramuscular (IM) injection is a shot. The needle goes into the muscle to deliver medication. This is usually done by a doctor or nurse. Sometimes, your doctor may teach you to inject yourself. IM injections are deeper than injections given under the skin.
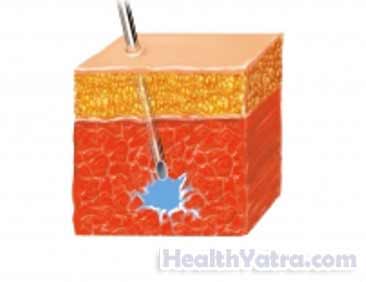
Reasons for Procedure
Some medications are better absorbed when given in the muscle. Other medications may be given in the muscle if you are unable to take them by mouth.
Some examples of medications given using an IM injection:
- Certain antibiotics
- Certain contraceptive hormones
- Most vaccines
- Epinephrine injections for severe allergic reactions
Possible Complications
Complications associated with IM injections are:
- Bleeding, soreness, or redness at the site
- Allergic reaction to the medicatiom
- Rarely, the site may become infected
What to Expect
Prior to Procedure
- Make sure you have all of the items that you will need in front of you.
- Make sure that you have the right medication and that it has not expired.
- Wash hands with warm, soapy water before giving the injection.
- Select a site for injection. This should be an area on your body with a large muscle, such as the thigh.
- Cleanse the area with an alcohol wipe.
Description of Procedure
To inject yourself:
- Remove the needle cap.
- Smooth the skin with one hand.
- Hold the syringe the way you would a pencil. Insert the needle at a 90° angle to the skin. The needle should be completely covered by skin.
- Hold the syringe with one hand. With the other, pull back the plunger to check for blood in the syringe.
- If you see blood, do not inject. Withdraw the needle and start again at a new site.
- If you do not see blood, slowly press down on the plunger until it stops.
- Remove the needle from the skin.
- If there is bleeding at the site of injection, apply a bandage.
- Immediately put the syringe and needle into a container that is puncture-proof.
- Find out what services are available in your area for disposing of biological waste.
Will It Hurt?
Depending on the medication, there is usually some discomfort at the injection site. Soreness in the muscle is also common.
Tips for minimizing pain include:
- Inject medication that is at room temperature.
- Remove all air bubbles from the syringe before the injection.
- Relax the muscles in the injection area.
- Quickly break through the skin.
- Do not change the direction of the needle as it goes in or comes out.
- Do not reuse disposable needles.
Care After Injection
Follow your doctor’s instructions for general care.
Call Your Doctor
Call your doctor if any of the following occur:
- Difficulty giving yourself the injection
- A lot of pain
- Medication is injected into the wrong area
- Redness, swelling, increasing pain, excessive bleeding, or any discharge from the injection site
- Rash or hives develop
- Difficulty breathing
- Fever
If you think you have an emergency, call for medical help right away.
