Definition
Gangrene is the death of an organ or body tissue. When the blood supply is cut off, the tissue does not get enough oxygen and begins to die. If the gangrene is widespread, shock can occur.
There are three main types:
- Dry gangrene—lack of blood supply causes the tissue to dry up and slough off
- Wet gangrene—usually occurs when the tissue is infected with bacteria, tissue becomes moist and breaks down
- Gas gangrene—a particular type of bacteria (Clostridia) produces gas bubbles in the tissue
Causes
Causes of gangrene include:
- Infection, especially after surgery or injury
- Diabetes
- Any condition that blocks blood flow to tissue (such as, atherosclerosis)
Risk Factors
These factors increase your chance of developing gangrene. Tell your doctor if you have any of these:
- Smoking
- Alcohol use
- Traumatic injury, especially crushing injuries
- Wound infection after surgery
- Frostbite
- Burns
- Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes
- Raynauds disease
- Blood clots
- Ruptured appendix
- Hernia
- IV drug use
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Swelling
- Pain, followed by numbness when the tissue is dead
- Sloughing off of skin
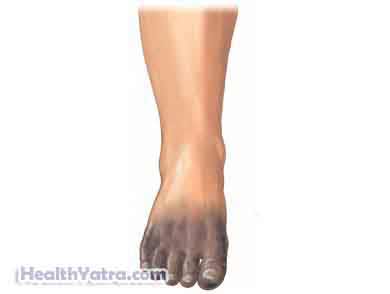
- Color changes, ranging from white, to red, to black
- Shiny appearance to skin
- Frothy, clear, watery discharge
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history and perform a physical exam.
Tests may include:
- Blood tests
- Tests of the discharge and the tissue
- X-ray—a test that uses radiation to take pictures of structures inside the body
- CT scan—a type of x-ray that uses a computer to make pictures of the inside of the body
- MRI scan—a test that uses magnetic waves to make pictures of the inside of the body
Treatment
Treatment of gangrene includes:
- Antibiotics—given through IV in a very potent form
- Blood thinners—given to prevent blood clots
- Debridement—surgical procedure to cut away dead and dying tissue, done to try to avoid gangrene from spreading
- Amputation— removal of severely affected body part (such as, toe or foot amputation, above-the-knee amputation)
- Hyperbaric oxygen treatment—involves exposing the affected tissue to oxygen at high pressure
Prevention
To help prevent gangrene:
- If you have diabetes, take good care of your hands and feet.
- If you need surgery, ask your doctor about taking antibiotics. This is especially true if you need intestinal surgery.
