Definition
Focal dystonia is an irregular movement disorder specific to one part of the body. In dystonia, muscle contractions cause irregular movements, twitches, tics, and twisted or repetitive postures. These may be continuous or off and on. The most common types of focal dystonia are:
- Blepharospasm—an eye twitch
- Cervical dystonia or spasmodic torticollis—affecting the neck
- Segmental cranial dystonia, also known as Meige syndrome—affecting the jaw, tongue and eyes
- Oromandibular dystonia—affecting the jaw
- Spasmodic dysphonia—affecting the vocal cords
- Axial dystonia—affecting the trunk
- Dystonia of the hand/arm, such as writer’s cramp
Focal dystonia can be treated. If you suspect you have this condition, contact your doctor.
Causes
Dystonias are caused by flaws of the basal ganglia of the brain. This is where messages that begin muscle contractions are processed. Factors that may cause focal dystonia include:
- Birth injury, such as lack of oxygen
- Infection
- Reactions to medicines
- Heavy metal poisoning
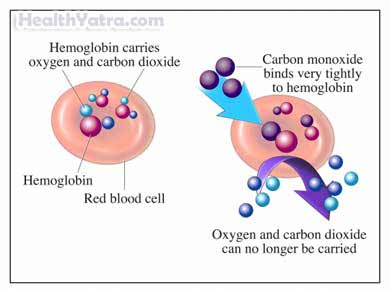
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Trauma
- Stroke
- Inherited abnormalities
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Other diseases
Risk Factors
Factors that can increase your risk of developing focal dystonia include:
- Family history of dystonia
- Recent exposure to an antinausea or antipsychotic medicine
Symptoms
If you have any of these symptoms, do not assume it is due to focal dystonia. These symptoms may be caused by other conditions:
- Eyelid spasms
- Rapid or uncontrollable blinking of both eyes
- Neck twisting
- Difficulty writing
- Foot cramps
- Pulling or dragging of a foot
- Tremor
- Voice or speech difficulties
Factors that may worsen dystonia include:
- Excitement or agitation
- Stress
- Talking
- Fatigue
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. You may be referred to a speech-language pathologist, physical or occupational therapists, and/or genetic counselors.
Tests may include:
- Your bodily fluids and tissue may need to be tested. This can be done with:
- Blood tests
- Urine tests
- Genetic tests
- Lumbar puncture
- biopsy
- The electrical activity of your muscles, nerves, and brain may need to be measured. This can be done with:
- Electromyography
- Nerve conduction study
- Electroencephalography
- Pictures may need to be taken of your head. This can be done with:
- MRI scan
- CT scan
- Transcranial ultrasound
- Other exams may include:
- Neurologic evaluation—to rule out other neurological disorders
- Eye exam

Treatment
Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment options include the following:
Medications
Certain medicines may help correct imbalances in neurotransmitters. Medicines used to treat dystonia include:
- Trihexyphenidyl
- Benztropine
- Procyclidine HCl
- Muscle relaxants
- Levodopa and carbidopa
- Bromocriptine
Anticonvulsant medicines may also help people with dystonia. Your doctor will balance treating your symptoms with reducing the risk of side effects from the medicines.
Botulinum Toxin Injections
Injecting botulinum toxin directly into the muscles affected by dystonia can weaken the muscle. This may help improve symptoms for 3-4 months.
Surgery
Surgery to cut the nerves leading to muscles affected by dystonia or removing the muscles may help reduce muscle contractions. In addition, surgery to destroy the small area within the brain that dystonia occurs from may stop or reduce the disorder. More recently, some success has been reported using surgically implanted deep brain stimulation to reduce symptoms of dystonia.
Prevention
There is no known way of preventing focal dystonia. To help reduce your chances of getting this condition, take steps to reduce your risk of infection, stroke, trauma, andcarbon monoxide or heavy metal poisoning. In addition, if you take any of the following medicines, talk with your doctor about your risk of developing dystonia as a side effect:
- Levodopa
- Bromocriptine
- Antipsychotics
- Metoclopramide
- Dilantin
- Calcium channel blockers
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- Ergotamines
- Antihistamines
