Definition
Cataract removal is a procedure to remove a cataract. A cataract is a clouding of the eye’s lens.
Reasons for Procedure
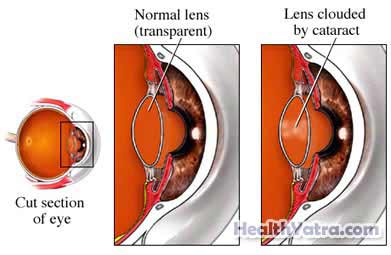
The lens of the eye is responsible for focusing images onto the back of the eye. It is normally transparent. With cataracts, the lens begins to cloud over time. This will gradually cause a loss in vision.
Cataract removal is done when the cataract is causing problems with vision. The surgery improves vision.
Possible Complications
Complications are rare, but no procedure is completely free of risk. If you are planning to have cataract surgery, your doctor will review a list of possible complications, which may include:
- Inflammation
- Infection
- Damage to the eye
- Decreased vision
- Increased eye pressure
- Droopy eyelid
- Need for more surgery
Some factors that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Poor overall health
- Bleeding disorders
- Infection
- History of trauma to the eye
What to Expect
Prior to Procedure
Your doctor may do the following:
- Complete eye exam
- An A-scan—a test using either sound waves or a laser to determine the strength of the replacement lens
- Administer eye drops
Anesthesia
Local anesthesia will be used. It will make the area numb.
Description of the Procedure
There are two main types of cataract removal.
Phacoemulsification Technique:
Most cataract removal surgeries are done using this technique. An ultrasound probe will break the cloudy lens into tiny fragments. A tiny incision will be made into the eye. The fragments will then be vacuumed out through the incision. A lens implant will be inserted to replace the affected lens. Stitches are often not needed. You may notice an improvement in your vision soon after surgery.
Extracapsular Technique:
An incision will be made in the eye. The cataract will be removed in one piece through the incision. The lens implant will be inserted to replace the affected lens. Because the incision will be larger, you will need stitches. The recovery will take longer with this technique.
After either procedure, a patch may be placed over your eye.
How Long Will It Take?
The process takes less than 1 hour.
Will It Hurt?
Most patients report no significant pain during the procedure. You may feel pulling or pressure sensations.
Post-procedure Care
At the Care Center
- You will have an eye examination.
- You will be given eye drops.
At Home
Be sure to follow your doctor’s instructions , which may include:
- Avoid any strenuous activity until cleared by your doctor. This includes lifting and bending.
- You will wear a patch on your eye after your surgery. Do not remove the patch until instructed by your doctor.
- Ask your doctor about how to wash your face and when it is okay to shower or bathe.
- You may be given an antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops to use for several weeks after your surgery. Use these eye drops as prescribed. Store them as advised by your pharmacist or doctor. Most anti-inflammatory drops need to be shaken very well prior to each time you put them in your eyes.
- Do not drive or operate machinery until advised by your doctor.
- Take pain medicines as recommended by your doctor.
- Your doctor may ask you to wear an eye shield at night.
- Make it a habit to wear UV-protecting sunglasses when you are outside.
You should notice improvements in your vision, although at first your vision may actually be worse than prior to the surgery. Every eye heals differently. One eye may heal more quickly or slowly than the other. Since each lens is individually fitted for each patient, you will likely need weaker glasses or contacts. You may not need them at all after this procedure.
Call Your Doctor
After arriving home, contact your doctor if any of the following occurs:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills
- Change in vision
- Redness, swelling, increasing pain, bleeding, or discharge from the affected eye
- Visual disturbances, such as double vision, flashes of light, floaters, part of the field of vision is missing, or eye pressure
In case of an emergency, call for medical help right away.
