Definition
Prosthetic heart valve thrombosis is a rare but serious complication of a heart valve replacement procedure. The complication occurs when a blood clot called a thrombus is attached to or near a prosthetic heart valve. This can obstruct blood flow or interfere with the function of the valve. This condition can be life-threatening. Seek medical attention right away if you think you have prosthetic heart valve thrombosis.
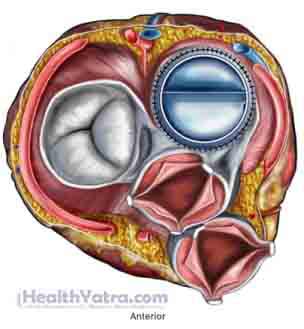
Heart Valves With Prosthetic Replacements
Causes
Prosthetic heart valve thrombosis is thought to result from an interaction between components of blood and the prosthesis or blood flow in and around the prosthesis.
Risk Factors
Factors that may increase your chance of developing prosthetic heart valve thrombosis include:
- Inadequate anticoagulant/blood thinning therapy after a valve transplant
- Prosthesis located at the mitral valve in the heart
- Atrial fibrillation
- Drugs such as contraceptives
- Cancerous tumors
- Systemic diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus or inflammation and damage to various body tissues, including joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and brain
- Reduced cardiac pumping—possibly from heart failure
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty breathing while lying down
- Swelling
- Fatigue
- Difficulty exercising
- Chest pain, burning, or pressure
- Nausea
- Numbness
- Loss of consciousness
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam may be done.
Images may need to be taken of your heart. This can be done with:
- Echocardiogram
- Fluoroscopy
Your bodily fluid may need to be tested. This can be done with blood tests.
Treatment
Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment options include:
Thrombolysis
The first line of therapy is usually thrombolysis, which uses medications to break up abnormal blood clots.
Anticoagulation Therapy
Anticoagulant medications are used to control clotting. Anticoagulation therapy may be used alone in people with small clots that are not obstructing the heart valve.
Valve Replacement
In some cases, surgery to replace the valve may be necessary.
Prevention
In people who have prosthetic heart valves, antithrombotic therapy is the best proven way to reduce the risk of prosthetic heart valve thrombosis.
