Definition
Loss of voice (also called aphonia) may take several different forms. You may have a partial loss of your voice and it may sound hoarse. Or, you may have complete loss of your voice and it may sound like a whisper. Loss of voice can come on slowly or quickly depending on the cause.
Aphonia is different than aphasia, which is a language disorder.
Causes
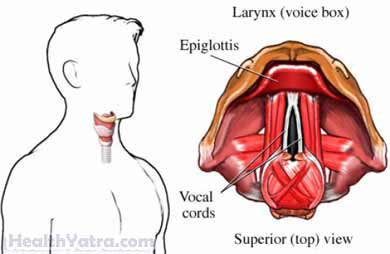
Aphonia is usually due to problems with the voice box (called the larynx). However, there can be other causes, including:
- Conditions that affect the vocal cords or airway. This may involve injury, swelling, or disease, such as:
- Laryngitis caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection
- Vocal abuse (yelling or talking excessively)
- Exposure to airborne irritants, such as smoke or air pollution
- Acid reflux (eg, heartburn)
- Thickening of the vocal chords
- Nodules or polyps on the vocal chords
- Muscle tension dysphonia
- Damage to the nerves that affect how the larynx functions
- Laryngeal or thyroid cancer
- Removal of larynx due to cancer
- Breathing problems that affect the ability to speak
- Neurological disorders (eg, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis)
- Psychological conditions (eg, hysterical aphonia)
Risk Factors
Risk factors that increase your chance of developing aphonia include:
- Overusing your voice (eg, speaking until you are hoarse)
- Behaviors that abuse your vocal chords, such as smoking, which also puts you at a higher risk for cancer of the larynx
- Having surgery on or around the larynx
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Inability to speak or inability to speak above a whisper
- Hoarseness
- Spasm of vocal cords
- Throat pain
- Difficulty swallowing (Food or fluids may go into the lungs.)
When Should I Call My Doctor?
Call your doctor if you:
- Have hoarseness that is not getting better after two weeks
- Have complete loss of voice that lasts more than a few days
- Have hard, swollen lymph nodes
- Have difficulty swallowing
- Cough up blood
- Feel a lump in your throat
- Have severe throat pain
- Have unexplained weight loss
When Should I Call for Medical Help Right Away?
Call for medical help right away or go to the emergency room if you: .
- Suddenly lose your ability to speak—This may be a sign of a head injury or astroke.
- Are having trouble breathing
If you think you have an emergency, call for medical help right away.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done.
The cause of your symptoms may not be obvious. You may be referred to a ear, nose, and throat doctor. This doctor may use an instrument called a laryngoscope to examine your vocal cords. Other tests may also be done to evaluate your voice function.
If your doctor is concerned that there may be a neurological or psychological cause, you may be referred to other specialists.
Treatment
General measures that can help ease laryngitis include:
- Resting your voice
- Avoiding smoking
- Staying hydrated
- Using a cool mist humidifier
- Taking nonprescription pain relievers (eg, acetaminophen , ibuprofen ) as needed
Other treatments depend on the specific cause, such as:
- Participating in voice therapy if your loss of voice is due to voice overuse
- Taking medicine to control acid reflux
- Having surgery to remove growths
Prevention
Take the following steps to help reduce your chance of getting aphonia:
- If you smoke, quit.
- If you drink, limit your intake.
- Limit your exposure to fumes and toxins.
- Avoid talking a lot or yelling.
- Avoid whispering
- Learn vocal techniques from a voice therapist if you have to speak a lot for your job.
- Get treatment for conditions that may cause loss of voice.
