Definition
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a group of inherited disorders. These disorders affect of the connective tissues. This type of tissue is found all over the body. There are at least six different varieties of EDS. They are classified by the type of tissue most affected and how it is inherited.
Causes
EDS is caused by a problem in the genetic material. It mainly affects the genes that create connective tissue.
Most types of EDS affect the production of collagen. Collagen is an important part of connective tissue. It gives the tissue strength and allows it to stretch.
Risk Factors
Having family members with EDS increases your chance of EDS.
Symptoms
The symptoms of EDS can vary. Some may have very mild symptoms. Other may have very severe and debilitating symptoms.
The most common symptoms of EDS include problems with the joints and skin. Joints are loose and unstable which can lead to:
- Swelling
- Sprains
- Dislocations
- Hyperextension
- Arthritis
- Development of flat feet
- Deformities of the thoracic spine, such as scoliosis (curvature of the spine) and kyphosis (a thoracic hump)
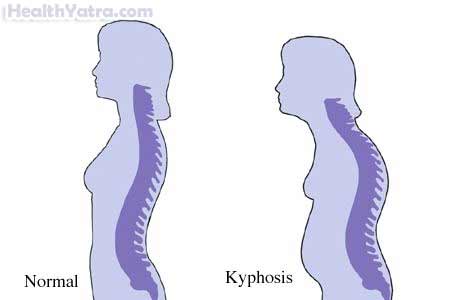
Skin is soft, fragile, and can stretch far too easily. This can lead to problems such as:
- Easy bruising
- Minor injuries turning into gaping wounds
- Slow and poor wound healing
- Difficulty suturing skin because skin tends to tear
- Skin scarring from wounds or stretching
- Fleshy outgrowths on top of scars
- Calcified nodules under the skin
- Increased risk of surgical complications
Other symptoms depend on the type of EDS you have. EDS can cause problems with:
- Eyes, such as:
- Nearsightedness (common in adults with EDS)
- Epicanthic fold—fold of skin on either side of the nose may cover the inner corner of the eye (common in children with EDS)
- Fragile sclera—the white outer coat of the eyeball
- Hole in the globe of the eye (rare)
- Lung—due to loss of normal elastic tissue
- Bones and muscles—such as chronic pain
- Blood vessels—weak tissue can lead to aortic aneurysms and rupture of blood vessels
- Blood clotting—can lead to easy bruising and bleeding
- Heart valves—such as mitral valve prolapse
- Gums—bleeding and diseases
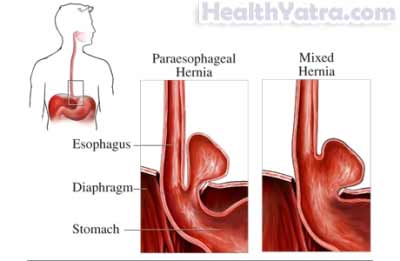
- Gastrointestinal system, such as:
- Hernias
- Diverticulosis
- Perforation or bleeding along the gastrointestinal tra
- Pregnancy, such as:
- Premature birth
- Early rupture of membranes
- Bleeding during pregnancy and excessive bleeding during or after childbirth
- Uterine rupture
- Higher complications from procedures
Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. This is usually enough to diagnosis EDS in most. When the diagnosis is uncertain, tests may include:
- Skin biopsy—to look for abnormalities in the connective tissue
- Detection of specific biochemical defects—available for certain types of EDS
Treatment
There is no known cure for EDS. Treatment may be needed to manage symptoms and or to try to prevent complications.
Treatment of Symptoms
Treatment will depend on your type of EDS and how severe it is.
For complications of the skin:
- Vitamin C supplements are possibly helpful in certain subtypes of EDS. It may help to decrease skin bruising and improve wound healing.
- Special care will be taken when repairing skin wounds. This may help to prevent or decrease scarring.
For musculoskeletal complications:
- Medication may help control pain.
- Surgery may be done to repair joint damage.
Some potential problems will need to be monitored. This includes patients at risk for blood vessel complications. Your doctor may ask for regular testing to examine major blood vessels.
Blood transfusions may be needed for severe bleeding.
Treatment to Reduce the Risk of Harm
Certain steps may help you reduce the chance of complications. Talk to your doctor about step that may help you such as:
- Wear joint braces.
- Do muscle strengthening exercise.
- Consider physical therapy to help strengthen muscles and joints.
- Wear sunscreen daily.
- Avoid activities that may cause injury, bruising, or over-extending your joints.
- Children may be asked to wear protective gear during activity.
- Talk to your doctor about possible pregnancy complications.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent EDS once a person is born. If you have EDS or have a family history of the disorder, consider genetic counseling when deciding to have children. The counselor can talk to you about the risk of your child having EDS.
Keywords :
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Definition, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Causes, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Symptoms, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Complications, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Surgery Cost in India, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Treatment Hospital in India, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Treatment in India, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Doctors in India, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Meaning in Hindi, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Meaning in Bengali, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Meaning in Arabic, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Treatment cost in 2024, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Hospital in India, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Treatment Near Me, 23 signs you grew up with ehlers-danlos syndrome, ehlers-danlos syndrome symptoms, ehlers-danlos syndrome supportive therapy, ehlers-danlos syndrome test, ehlers-danlos syndrome treatments, ehlers-danlos syndrome medication, ehlers-danlos syndrome types, ehlers-danlos syndrome diagnosis
